The Comprehensive Guide to Paraxanthine: What You Need to Know About the Caffeine Metabolites
Find out everything you need to know about paraxanthine, the chemical compound produced when the body breaks down caffeine. From its effects on the body to its role in the effects of caffeine, this comprehensive guide covers it all.
Introduction to Paraxanthine: What is It and How is it Produced?
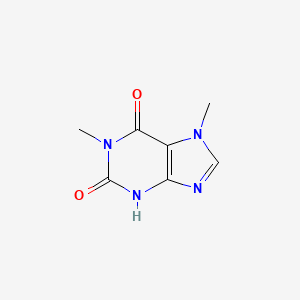
Paraxanthine is a chemical compound that is produced when the body breaks down caffeine. It is one of the main metabolites of caffeine and is responsible for many of the effects of caffeine on the body. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what paraxanthine is, how it is produced, and how it affects the body.
Caffeine is a stimulant that is found in a variety of foods and beverages, including coffee, tea, chocolate, and some medications. When caffeine is consumed, it is absorbed into the bloodstream and then metabolized by the liver. One of the main enzymes responsible for caffeine metabolism is cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2). This enzyme converts caffeine into several different metabolites, including paraxanthine.
What are the Effects of Paraxanthine?
Paraxanthine is thought to have a number of effects on the body, including:
Increased alertness and mental performance: Paraxanthine is thought to enhance cognitive function and improve mental performance by stimulating the central nervous system. It does this by increasing the levels of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain.
Improved physical performance: Paraxanthine may improve physical performance by increasing the availability of fatty acids for energy and increasing the production of heat in the body. This can help to improve endurance and strength during exercise.
Cardiovascular effects: Paraxanthine may have some effects on the cardiovascular system, including increasing heart rate and blood pressure. However, the exact nature of these effects is not fully understood and more research is needed to clarify the role of paraxanthine in the cardiovascular system.
Thermogenic effects: Paraxanthine may contribute to the thermogenic (heat-producing) effects of caffeine, which may help to increase the rate of fat burning in the body. This can help to promote weight loss and improve body composition.
How Much Caffeine Do You Need to Consume to Produce Paraxanthine?
The amount of caffeine needed to produce paraxanthine varies depending on the individual and their enzyme activity. Some people may produce significant amounts of paraxanthine with just a small amount of caffeine, while others may need to consume higher amounts to produce the same amount of paraxanthine.
Factors that can affect the production of paraxanthine include genetics, age, gender, and the presence of other medications. For example, some medications can inhibit the activity of CYP1A2, which can affect the production of paraxanthine.
Are There Any Risks Associated with Paraxanthine?
While paraxanthine is generally considered safe, excessive caffeine consumption can lead to negative side effects, including jitters, anxiety, insomnia, and stomach upset. It is important to consume caffeine in moderation to avoid these side effects.
The recommended daily intake of caffeine for adults is 400 mg per day, which is equivalent to about four cups of coffee.
As for paraxanthine alone the risks are still being studied.
The Role of Paraxanthine in Caffeine Addiction and Withdrawal
Caffeine is the most widely consumed psychoactive substance in the world, and many people rely on it to help them stay alert and focused. However, like any psychoactive substance, caffeine can be addictive, and withdrawal symptoms can occur when caffeine intake is suddenly stopped.
Paraxanthine is thought to play a role in caffeine addiction and withdrawal. When caffeine is consumed, it is converted into paraxanthine and other metabolites, which can bind to receptors in the brain and produce a feeling of alertness and increased mental performance. Over time, the brain may become accustomed to the presence of these compounds and may rely on them to function normally.
When caffeine intake is suddenly stopped, the brain may not have enough of these compounds, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can be relieved by consuming caffeine again, which can reinforce the cycle of addiction.
Paraxanthine and Athletic Performance: What You Need to Know
Caffeine is a popular performance-enhancing substance among athletes, and paraxanthine is thought to contribute to its effects on the body. Caffeine and paraxanthine are thought to improve physical performance by increasing the availability of fatty acids for energy and increasing the production of heat in the body. This can help to improve endurance and strength during exercise.
However, the effects of caffeine and paraxanthine on athletic performance can vary depending on the individual and the amount consumed. Some people may experience a boost in performance with small amounts of caffeine, while others may need higher amounts to see the same effects. It is important to note that caffeine is a banned substance in some sports, and athletes should be aware of the rules and regulations surrounding its use.
Paraxanthine and Health: What is the Current Research Saying?
While paraxanthine is generally considered safe, more research is needed to fully understand its effects on health. Some studies have suggested that caffeine and paraxanthine may have a number of health benefits, including:
Reducing the risk of Parkinson’s disease: Some studies have suggested that caffeine and paraxanthine may help to reduce the risk of Parkinson’s disease, a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement.
Reducing the risk of stroke: Some studies have found that caffeine and paraxanthine may help to reduce the risk of stroke, especially in women.
Improving memory and cognitive function: Some research has suggested that caffeine and paraxanthine may improve memory and cognitive function, especially in older adults.
Reducing the risk of certain types of cancer: Some studies have found that caffeine and paraxanthine may help to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer.
It is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the potential health benefits of caffeine and paraxanthine, and more studies are needed to confirm these findings. It is also important to consume caffeine in moderation to avoid negative side effects and to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your caffeine intake.
Conclusion: What We Know About Paraxanthine
In conclusion, paraxanthine is a chemical compound that is produced when the body breaks down caffeine. It is one of the main metabolites of caffeine and is responsible for many of the effects of caffeine on the body. Paraxanthine is thought to have a number of effects on the body, including increased alertness and mental performance, improved physical performance, and thermogenic effects. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential health benefits and risks of paraxanthine. It is important to consume caffeine in moderation to avoid negative side effects and to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your caffeine intake.